[IT Note] Resolution of Digital TV
What is the resolution of Digital TV?
I've worked in video technology for analog TV as a hardware engineer, but it was coming digital revolution to video industry in late 1990. The DVD was fast, then digital TV tooked more time because of quite huge investment to all broadcasting system and commercial TV.
The resolution of Digital TV can vary depending on the specific format and standard being used.
The most common digital TV standard is the High Definition Television (HDTV), which has a resolution of 1920 pixels x 1080 lines (also known as 1080p). However, there are also other digital TV standards, such as Standard Definition Television (SDTV) with a resolution of 720 pixels x 480 lines (480p) and Ultra High Definition Television (UHDTV) with a resolution of 3840 pixels x 2160 lines (2160p or 4K).
It's worth noting that the resolution is just one aspect of the picture quality. Other factors such as color depth, frame rate, and compression technology also play a role in determining the overall quality of the image.
But it was replaced existing NTSC (National Television Systems Committee) system to ATSC (Advanced Television Systems Committee) at US on June 12, 2009, Canada in 2011, South Korea in 2012 and Mexico in 2015. And existing PAL (Phase Alternating Line) system was changed to DVB (Digital Video Broadcasting) at European, Middle East, Africa & Asia.
The digital video brought two visible things:
1) Different aspect from 4:3 to 16:9 as long vertical line
2) End of HD (High Definition) for display, broadcast & film
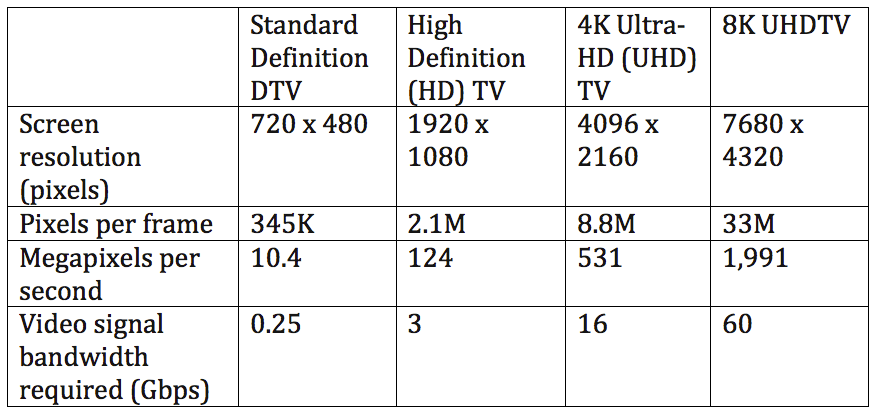
The pixel memory size per frame are dramatic increase from 2.1M in HD, 8.8M in 4K UHD and 33M in 8K UHD.
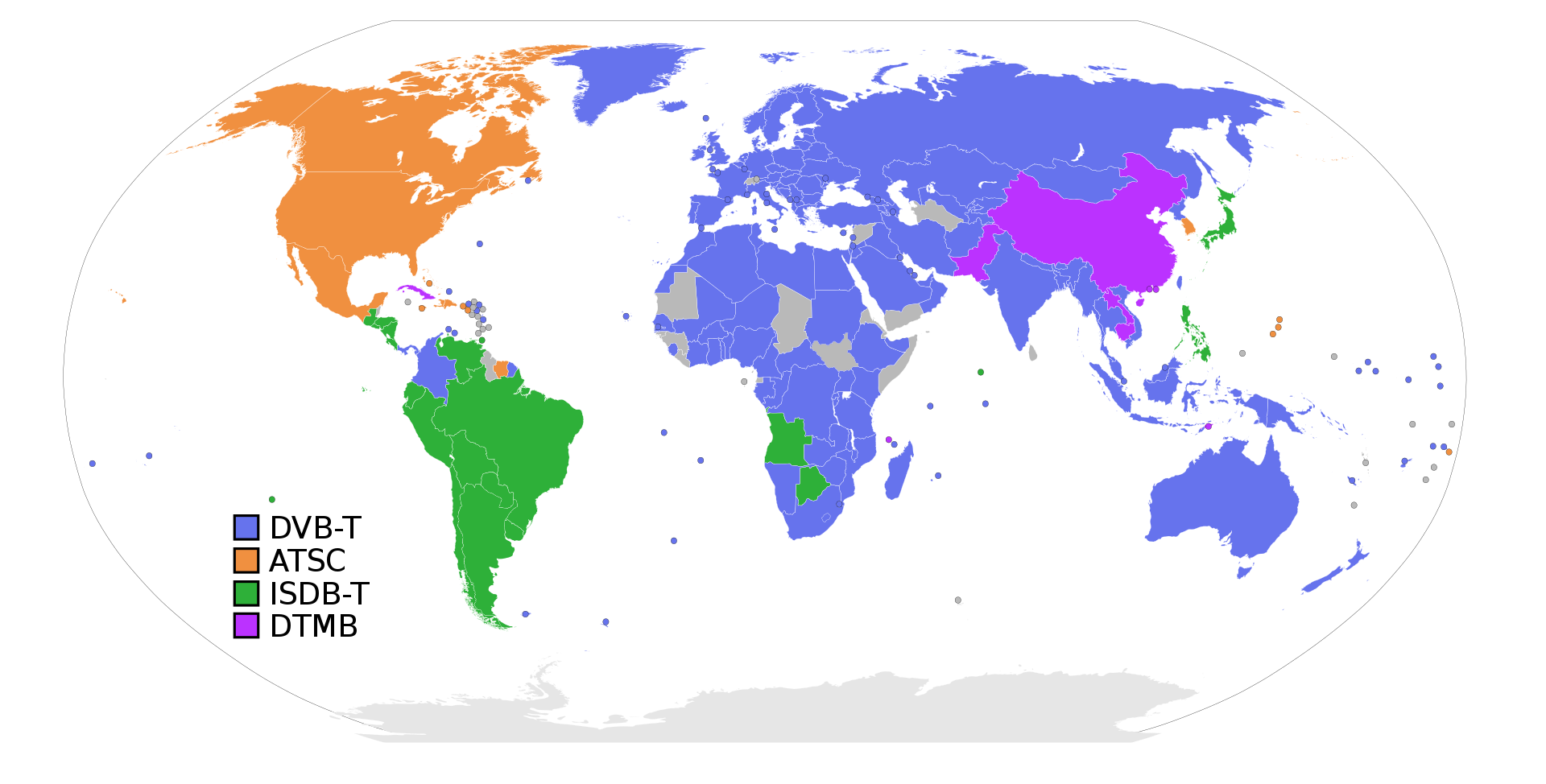
I've developed the video product based NTSC/PAL and digital video standards ATSC/DVB, but I'm not sure why PAL & DVB were more popular than NTSC & ATSC led by US. The map of TV broadcasting are same from analog to digital.
As for why PAL and DVB were more popular than NTSC and ATSC, there are several reasons. PAL and DVB were developed in Europe and were adopted by many countries in Europe and Asia. They also offer better picture quality and sound than NTSC and ATSC. Additionally, PAL and DVB are more flexible and can support a wider range of video and audio formats. Finally, the switch to digital broadcasting offered an opportunity for countries to adopt new standards, and many countries chose to adopt PAL and DVB over NTSC and ATSC.