영어 자음 발음 총정리: 파열음, 마찰음, 구개음, 비음, 액음, 반모음, 무엇인가요?**
[미국영어] 영어자음 발음 총정리: 파열음, 마찰음, 구개음,.. 에 대해 리뷰하려고 합니다.
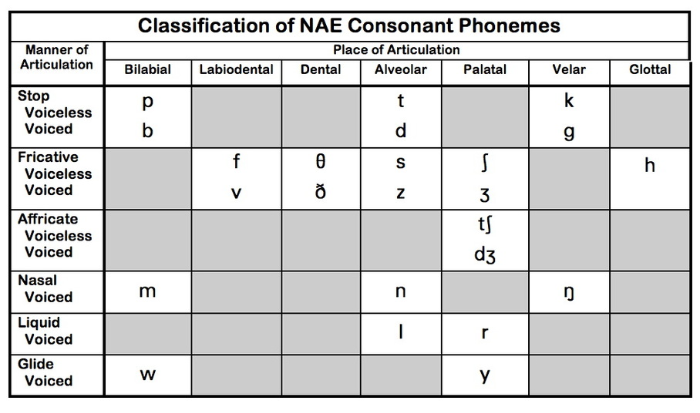
영어 자음 구성 : 6개 발음 카테고리, 24개 자음
얼마전 한국에서 유행이 되었던 Phonics 가 있는데, 미국 아이들이 영어 발음을 정확히 배우기 위해서, 주로 유치원에서 시행되는 발음 프로그램입니다.
한국어를 모국어로 하는 성인이 영어를 배우는 경우에는, 한국어 발음에 기초한 자음과 모음 발음으로 어색한 영어 발음이 되는 한계가 있습니다.
하지만, 미국 어린이들이 배우는 English Phonics로는 미국 네이티브들이 발음하는 주요 자음과 모음을 체득하게 되면서, 발음이 상당히 좋아지는 효과가 있지요.
영어 자음은 6개 발음 카테고리에 24개 자음으로 구성되어 있습니다.
6개 발음 카테고리는 파열음, 마찰음, 구개음, 비음, 액음, 반모음입니다.
영어 발음기호는 IPA (International Phonetic Alphabet chart) 기준을 적용했습니다.
파열음 Plosive or Stop
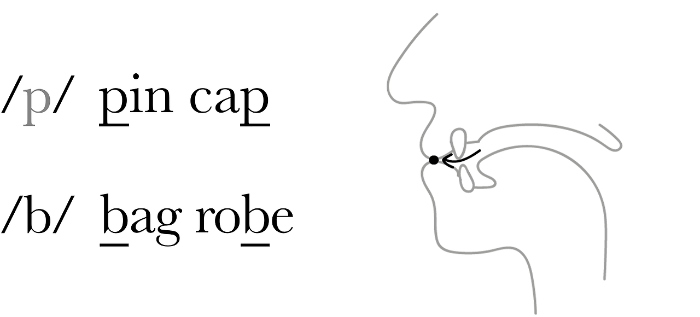
파열음 자음은 공기 흐름을 완전히 차단한 다음에 풀어내어 갑작스런 공기 방출로 이루어진 소리입니다. 발음하기 위해서는 성문을 완전히 막아서 공기가 흐르지 못하도록 한 다음 갑자기 공기를 방출시켜 소리를 만듭니다.
Plosive consonants, also known as stops, are sounds produced by completely blocking airflow and then releasing it. This results in a sudden release of air. To articulate a plosive, you obstruct the airflow in the vocal tract completely, then release it with a sudden burst. This creates a distinct sound.
Examples: /p/, /b/, /t/, /d/, /k/, /g/ in English (as in "pat", "bat", "tip", "dig", "cat", "gag")
마찰음 Fricative
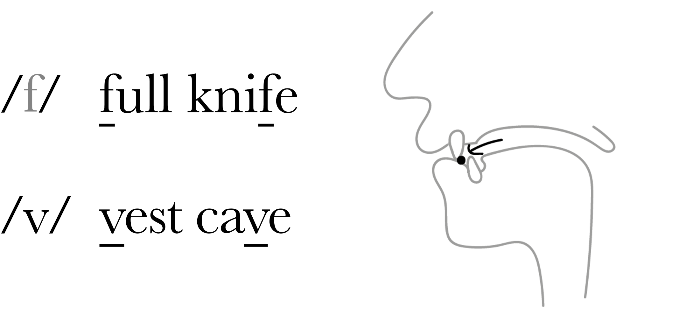
마찰음 자음은 발음기관 사이에서 마찰을 일으키도록 공기 흐름을 좁히는 소리입니다. 마찰음은 발음기관 (혀와 이를 등) 사이를 좁혀 공기가 흐를 수 있는 경로를 만들어 발음을 만듭니다.
Fricative consonants are produced by narrowing the airflow in the vocal tract to create friction between articulators.
Fricatives are formed by allowing air to flow through a narrow channel created by articulators (such as the tongue and teeth), producing a turbulent noise.
Examples: /f/, /v/, /s/, /z/, /ʃ/, /ʒ/ in English (as in "fun", "van", "sip", "zip", "shoe", "measure").
구개음 Affricate
구개음 자음은 파열음으로 시작하여 마찰음으로 끝나는 소리입니다. 구개음은 파열음과 마찰음의 요소가 결합되는데, 파열음처럼 성문을 완전히 막은 다음에 서서히 공기를 방출하면서 마찰음을 만듭니다.
Affricate consonants start with a plosive closure and finish with a fricative release. Affricates combine elements of both plosive and fricative sounds. They begin with a complete closure of the vocal tract, like plosives, and end with a gradual release accompanied by friction, like fricatives.
Examples: /tʃ/, /dʒ/ in English (as in "church", "judge").

비음 Nasal
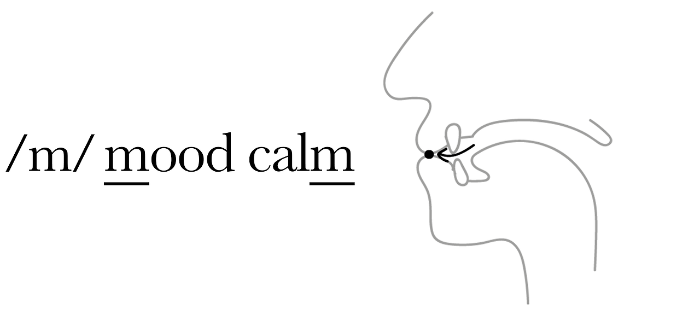
비음 자음은 입을 닫은 상태에서 공기가 코를 통해 나가는 소리입니다. 비음 자음은 입을 닫은 상태에서 후두개를 내림으로써 코를 통해 공기가 나가도록 합니다.
Nasal consonants are produced by allowing air to escape through the nose while the mouth is closed. Nasal consonants are formed by lowering the velum (the soft part of the roof of the mouth), allowing air to pass through the nasal cavity while the oral cavity remains closed.
Examples: /m/, /n/, /ŋ/ in English (as in "moo", "no", "sing").
액음 Liquid
액음 자음은 음성관에서 부분적인 막음을 만들어 주변을 흐르도록 하는 소리입니다. 액음은 음성관에서 혀를 부분적으로 막아주어 공기가 흐르도록 만드는 소리로, 다른 자음과 비교하여 공기의 흐름이 덜 막힌다는 특징이 있습니다.
Liquid consonants involve a partial closure in the vocal tract, allowing air to move around the sides. Liquids are formed by allowing the tongue to make a partial closure in the vocal tract, creating a space for air to flow around. They are called liquids because the airflow is less obstructed compared to other consonants.
Examples: /l/, /r/ in English (as in "let", "run").
반모음 Glide
반모음, 또는 글라이드 자음은 모음과 모음 사이에서 부드러운 전이를 만드는 소리입니다. 글라이드, 즉 반모음은 발음기관이 더 좁은 위치에서 더 열린 위치로 서서히 이동함으로써 모음과 모음 사이의 부드러운 전이를 만듭니다. 종종 음절 내에서 모음 사이에서 전이하는 소리로 작용합니다.
Glide consonants involve a smooth transition from one vowel-like sound to another. Glides, also known as semivowels, are produced by a gradual movement of the articulators from a more constricted position to a more open one, resembling a vowel-like sound transition. They often function as transitional sounds between vowels within syllables.
Examples: /j/, /w/ in English (as in "yes", "we").

[미국영어] 영어자음 발음: b 사운드 vs p 사운드
[미국영어] 영어자음 발음: b 사운드 vs p 사운드 영어자음 발음: b 사운드 vs p 사운드 (Demo Video) 영어자음 발음: b 사운드 vs p 사운드 [미국영어] 영어자음 발음: b 사운드 vs p 사운드 에 대해 리뷰하
stephan-review.tistory.com
[미국영어] 영어자음 발음: th 사운드, /θ/ think vs /ð/ those
[미국영어] 영어자음 발음: th 사운드, /θ/ think vs /ð/ those TH SOUNDS (Intro Video) TH SOUNDS (source: youtube.com) [미국영어] 영어자음 발음: th 사운드, /θ/ think vs /ð/ those 에 대해 리뷰하려고 합니다. th 스펠링
stephan-review.tistory.com